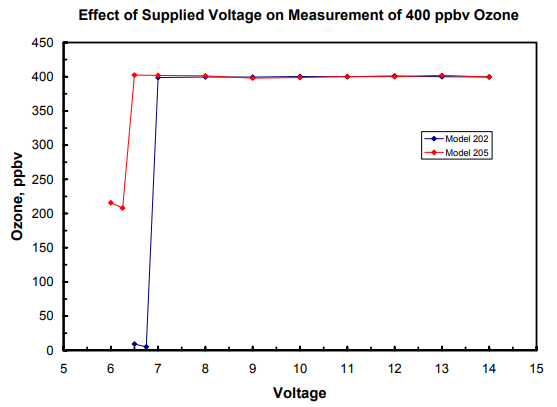
Both Model 202 and Model 205 Ozone Monitors will make accurate measurements in the applied voltage range of 7-14 V.
Effect of Voltage on Ozone Measurements by Model 202 and 205 Ozone
Monitors
Date: 5 May 2006
Author: John Birks
Question Addressed
2B Tech Ozone Monitors are often operated using external batteries. As the
voltage of a battery declines, the instrument will fail at some point. This technical
note determines over what voltage range the instruments can be reliably
operated.
Experimental
In separate experiments, Model 202 and Model 205 Ozone Monitors sampled air
containing 400 ppbv ozone from the 2B Technologies calibration manifold.
Ozone was also measured by the 2B Tech Standard Reference Instrument.
Power was supplied by a variable voltage external power supply. Average ozone
measurements were recorded and plotted versus supplied voltage in the range 6-
14 volts. Inlet flow rates also were measured as a function of applied voltage.
Results
The measured ozone mixing ratios were found to be independent of applied
voltage in the range 7-14 volts. At voltages below 6.75 volts for the Model 205
and 7.00 volts for the Model 202, measured ozone values dropped precipitously.
The cause of failure was determined to be insufficient voltage to drive the
solenoid valves. A graph showing the results is given below.
Sample volumetric flow rates varied from 1,260 cc/min at 7 V to 2,140 cc/min at
14 V for the Model 205 and 447 cc/min at 7 V to 780 cc/min at 14 V for the Model
202.
The precipitous drop in measured ozone concentration at low voltages below 7 V
was found to be due to failure of the solenoid valve to switch rather than a
reduction in flow rate.
Conclusions
Both Model 202 and Model 205 Ozone Monitors will make accurate
measurements in the applied voltage range of 7-14 V.